Preparing for a Salesforce Technical Architect interview involves a deep understanding of Salesforce’s platform, architecture, and best practices.
Here’s a broad set of questions divided into different categories relevant to a Salesforce Technical Architect:
General Understanding & Conceptual Knowledge
- What is a Technical Architect’s role in a Salesforce implementation?
- Can you explain the MVC architecture as it relates to Salesforce?
- What are the key considerations for data migration in Salesforce?
- Describe the concept of multi-tenancy in Salesforce.
- How do you ensure the scalability of a Salesforce solution?
- What is the difference between Salesforce Classic and Lightning Experience in terms of architecture?
- Explain the role of API in Salesforce integrations.
- What are the main security features in Salesforce that architects should know about?
Salesforce Products and Features
- How would you describe the function of Salesforce Sales Cloud to a stakeholder?
- What are the architectural considerations for implementing Service Cloud?
- Can you detail how Salesforce Marketing Cloud integrates with other Salesforce clouds?
- Explain the use of Salesforce Commerce Cloud and its impact on system architecture.
- What are the benefits and challenges of implementing Salesforce CPQ?
- How does Salesforce Einstein change the architecture of a Salesforce solution?
- What is Salesforce Shield and why is it important for security?
Design and Implementation
- How do you handle large data volumes (LDV) in Salesforce?
- What strategies would you use for long-running operations in Salesforce?
- Explain the process of selecting between triggers, batch Apex, and workflow rules.
- How would you design a robust error handling system in Salesforce?
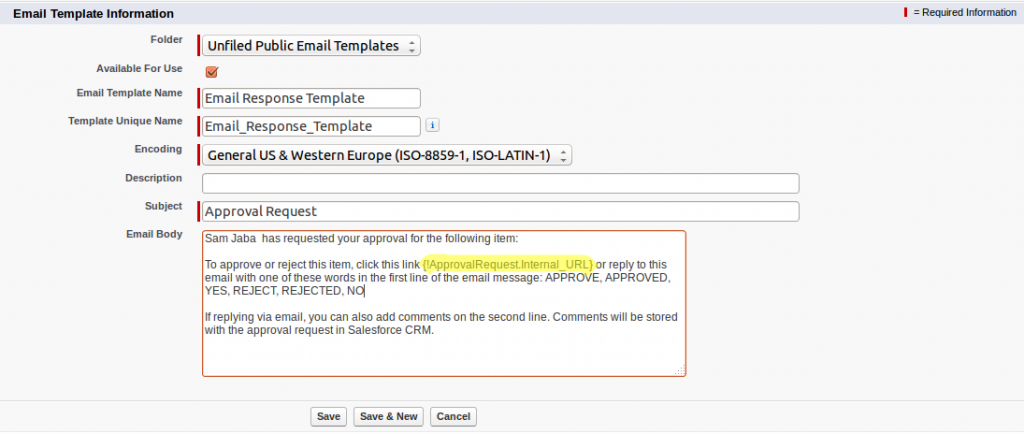
- Describe a scenario using Platform Events and when they would be necessary.
- What are best practices for using custom settings and custom metadata types?
- How do you ensure a Salesforce design is optimized for mobile users?
Data Management
- What are the implications of data skew in Salesforce and how do you manage it?
- Describe strategies to maintain data quality in a Salesforce instance.
- How would you plan and execute a large scale data archiving strategy in Salesforce?
- What tools and techniques are available for data backup in Salesforce?
- Explain the role of external objects in Salesforce.
Integration and Middleware
- What are the typical integration patterns used with Salesforce?
- How do you choose between REST and SOAP APIs for integration?
- What considerations should be made when integrating Salesforce with ERP systems?
- Describe how you would secure data transmitted between Salesforce and external systems.
- What is an Integration User, and when would you use it?
- What are some common performance bottlenecks in Salesforce applications?
- How would you use the Developer Console to troubleshoot performance issues?
- What are the limitations of Salesforce report performance and how can you overcome them?
- Describe the process to optimize SOQL queries.
- How do you use Salesforce’s Execution Governors and Limits?
Testing and Deployment
- What is the recommended approach for deploying changes in Salesforce?
- How do you manage version control with Salesforce development?
- What are the best practices for Salesforce environment management?
- Describe strategies for effective test automation in Salesforce.
- How do you ensure a smooth user acceptance testing (UAT) process?
Advanced Technical Scenarios
- Describe an approach for handling multi-language and multi-currency support in Salesforce.
- How would you architect a solution for real-time analytics in Salesforce?
- What are considerations for implementing Single Sign-On (SSO) with Salesforce?
- How do you approach the design of a Salesforce solution that must comply with GDPR?
- What are the considerations for using Blockchain technology in a Salesforce solution?
This list gives you a broad range of questions that cover different aspects of a Salesforce Technical Architect’s responsibilities.
Answers:
1. What is a Technical Architect’s role in a Salesforce implementation?
The role of a Technical Architect in a Salesforce implementation involves overseeing the solution’s overall architecture. They ensure that the solution aligns with business requirements and integrates seamlessly with other systems. Their responsibilities include designing scalable and secure architectures, guiding best practices, and solving complex technical challenges.
2. Can you explain the MVC architecture as it relates to Salesforce?
In Salesforce, the Model-View-Controller (MVC) architecture separates the application into three interconnected components. The Model represents the database and includes objects and fields. The View is the user interface, including pages and components that display the model data. The Controller processes the business logic and handles user interactions. Salesforce implements this pattern to organize code and simplify development.
3. What are the key considerations for data migration in Salesforce?
Key considerations for data migration into Salesforce include:
- Data cleanliness: Ensuring data is clean and duplicate-free before migration.
- Mapping: Correctly mapping data fields from the source system to Salesforce fields.
- Volume: Managing large data volumes by using tools like the Bulk API.
- Testing: Thoroughly testing the migration process to prevent data loss and ensure integrity.
- Change management: Preparing the organization for changes in how data is accessed and managed.
4. Describe the concept of multi-tenancy in Salesforce.
Multi-tenancy in Salesforce means that multiple customers share the same infrastructure and platform although their data and configurations are kept separate. This architecture allows Salesforce to efficiently manage resources and upgrades across multiple clients, ensuring security and data privacy through a rigorous partitioning of tenant data.
5. How do you ensure the scalability of a Salesforce solution?
To ensure scalability in Salesforce, architects should:
- Design with scalable components like custom objects and applications that can handle increased volumes.
- Use asynchronous processing (e.g., batch jobs, future methods) to manage large operations.
- Implement efficient data management strategies to handle large data volumes.
- Regularly review and optimize code and queries for performance.
6. What is the difference between Salesforce Classic and Lightning Experience in terms of architecture?
Salesforce Classic uses a page-centric architecture where each interaction requires a server round-trip. Lightning Experience, however, is component-based, built on the Lightning Component Framework that encourages modular app development with dynamic client-side interactions. This modern approach improves performance, provides enhanced user interfaces, and facilitates easier customization.
7. Explain the role of API in Salesforce integrations.
APIs in Salesforce (e.g., REST, SOAP, Bulk, Streaming) play a critical role in integrations, allowing external systems to securely access Salesforce data and functionality. They enable real-time data synchronization, automation of processes, and expansion of Salesforce capabilities into other systems, essential for creating a connected ecosystem.
8. What are the main security features in Salesforce that architects should know about?
Key security features in Salesforce include:
- Profiles and Permission Sets to control user access to data.
- Field-Level Security to restrict access to specific fields.
- Organization-Wide Defaults and Sharing Rules to manage record access.
- Encryption, using Salesforce Shield for encrypting sensitive data at rest.
- Audit Trail to monitor changes made within the system.
9. How would you describe the function of Salesforce Sales Cloud to a stakeholder?
Salesforce Sales Cloud is a CRM platform designed to support sales processes. It enables organizations to store customer data, track sales opportunities, automate workflows, and manage customer interactions and relationships to increase sales efficiency and effectiveness.
10. What are the architectural considerations for implementing Service Cloud?
When implementing Service Cloud, considerations include:
- Integration with existing systems (e.g., ERP, marketing platforms).
- Configuring case management workflows for efficient resolution.
- Implementing Omni-Channel for routing cases to the right agent.
- Ensuring data security and compliance, especially for sensitive customer data.
- Scalability to handle varying volumes of service requests.
11. Can you detail how Salesforce Marketing Cloud integrates with other Salesforce clouds?
Salesforce Marketing Cloud integrates with other Salesforce clouds (like Sales Cloud and Service Cloud) through Salesforce Connect and API integrations. This allows for seamless sharing of data such as customer contact details, engagement history, and campaign responses, which enhances the consistency and relevance of marketing campaigns. The integration also enables triggering of customer journeys based on actions within Sales or Service Clouds, providing a unified customer experience.
12. Explain the use of Salesforce Commerce Cloud and its impact on system architecture.
Salesforce Commerce Cloud is designed to create unified, intelligent shopping experiences across all channels, whether online, mobile, or in-store. It impacts system architecture by necessitating robust, scalable integrations with inventory, order management, and customer databases. Commerce Cloud is often integrated with ERP systems and uses APIs to synchronize customer and order data, ensuring that all touchpoints have real-time access to accurate information.
13. What are the benefits and challenges of implementing Salesforce CPQ?
Benefits:
- Streamlines the quoting process, reducing errors and increasing speed.
- Supports complex pricing structures and automation of discounts, improving accuracy and efficiency.
- Enhances visibility into quoting and sales processes.
Challenges:
- Complexity of setup and configuration, especially for organizations with complex sales processes.
- Requires training for users due to its comprehensive features.
- Integration challenges with other systems, such as ERP or external pricing databases.
14. How does Salesforce Einstein change the architecture of a Salesforce solution?
Salesforce Einstein introduces AI capabilities into the Salesforce environment, allowing for smarter customer interactions and data-driven decisions. Architecturally, it requires considerations for data quality and volume, as AI models are only as good as the data they learn from. Integration points might need to be established or enhanced to gather comprehensive data inputs. Additionally, performance considerations must be managed to ensure the AI functionalities do not slow down the system.
15. What is Salesforce Shield and why is it important for security?
Salesforce Shield is a suite of security tools designed to enhance data protection, compliance, and governance for Salesforce applications. It includes features like Platform Encryption, Event Monitoring, and Field Audit Trail. Shield is crucial for organizations that handle sensitive data, as it provides tools to encrypt data at rest, monitor user activities in real-time, and maintain detailed audit histories up to ten years, helping organizations comply with regulatory requirements.
16. How do you handle large data volumes (LDV) in Salesforce?
Handling large data volumes in Salesforce involves strategies such as:
- Archiving old data that is not frequently accessed.
- Using indexing and optimized queries to improve data retrieval times.
- Employing Salesforce’s Big Objects for storing massive data sets that are infrequently accessed but need to be available.
- Utilizing skinny tables to improve performance in reports and SOQL queries.
- Implementing asynchronous processes (Batch Apex, Queueable Apex) for data operations that involve large datasets.
17. What strategies would you use for long-running operations in Salesforce?
For long-running operations, Salesforce architects use asynchronous processing methods like Batch Apex, Future Methods, and Queueable Apex to manage processes that exceed normal processing limits. These methods allow operations to run in the background, processing large data volumes without hitting governor limits. Additionally, leveraging Salesforce’s Bulk API for data-intensive tasks like data import or large updates is crucial.
18. Explain the process of selecting between triggers, batch Apex, and workflow rules.
Selection depends on the specific requirements:
- Workflow Rules are best for simple field updates, email notifications, or tasks that don’t require complex logic.
- Triggers are suitable for more complex operations that need to occur immediately after a record is created or updated and where the logic cannot be accomplished via workflows.
- Batch Apex is used when the operation needs to handle large data volumes that exceed the limits of what triggers can process in a single transaction, or when the task can be scheduled to run during off-peak hours.
19. How would you design a robust error handling system in Salesforce?
A robust error handling system in Salesforce should include:
- Try-Catch blocks in Apex to manage exceptions.
- Custom error logging to a custom object or external system.
- User-friendly error messages to inform end-users of issues without exposing sensitive system details.
- Integration error handling, ensuring that failures in external calls do not cripple user operations.
- Monitoring and alerts using tools like Event Monitoring and custom dashboard indicators for system health.
Platform Events are useful in scenarios where you need to communicate changes in Salesforce to external systems or between different parts of Salesforce asynchronously. For example, in a manufacturing process, an event can be published when a product assembly completes, which triggers downstream processes such as packaging and shipping, handled by different systems or components. This event-driven architecture helps decouple processes and enhances system scalability and responsiveness.
Custom Settings:
- Use custom settings for storing data that varies by organization or profile but does not change frequently, like system parameters or integration settings.
- Hierarchical custom settings can store data specific to an organization, profile, or user.
- They are cached, providing efficient access without counting against SOQL query limits.
Custom Metadata Types:
- Use custom metadata types to store data that needs to be deployable with packages, such as configurations that should be migrated with Metadata API.
- They are also cached and can be queried and managed via Metadata API, unlike custom settings.
- Useful for storing information that controls application behavior, such as mappings or flow definitions, which can be updated by administrators without deploying code.
22. How do you ensure a Salesforce design is optimized for mobile users?
To optimize Salesforce design for mobile users, consider the following practices:
- Use Salesforce Mobile SDK and Lightning Design System to ensure interfaces are responsive and provide a consistent user experience across devices.
- Simplify layouts, focusing on essential information and interactions to enhance usability on smaller screens.
- Optimize performance by minimizing the data transferred over mobile connections and implementing offline capabilities for critical functionality.
- Test on multiple devices and networks to ensure the application performs well in varied mobile conditions.
23. What are the implications of data skew in Salesforce and how do you manage it?
Data skew in Salesforce occurs when a single record (like an Account) has a very high number of related records (like Contacts), which can degrade performance. To manage data skew:
- Distribute ownership of records more evenly across multiple parent records to avoid having too many child records linked to a single parent.
- Use indexing and selective queries to improve performance.
- Consider splitting very large datasets into smaller, more manageable ones and using sharing rules thoughtfully to minimize overhead.
24. Describe strategies to maintain data quality in a Salesforce instance.
Strategies to maintain data quality include:
- Implement validation rules and required fields to ensure data completeness and accuracy upon entry.
- Use duplicate rules and matching rules to prevent and merge duplicate records.
- Regularly audit and cleanse data using data cleansing tools or built-in Salesforce reports to identify and correct inaccuracies.
- Educate users on the importance of data quality and provide training on how to enter and manage data properly.
25. How would you plan and execute a large scale data archiving strategy in Salesforce?
To plan and execute a large-scale data archiving strategy:
- Identify data that is no longer actively used but needs to be retained for historical or compliance reasons.
- Use data archiving tools like Salesforce Big Objects or external archiving solutions to store old data securely.
- Define and implement retention policies that specify how long different types of data should be kept before archiving or deletion.
- Ensure that archived data can be accessed or recovered when required, maintaining a balance between accessibility and performance.
For data backup in Salesforce, you can use:
- Salesforce’s Data Export service, which can be scheduled regularly to export data as backup files.
- Third-party backup solutions that provide more comprehensive features, such as automated backups, quick restore capabilities, and fine-grained data recovery.
- Using APIs (Data Loader or Workbench) to periodically extract data for backup.
27. Explain the role of external objects in Salesforce.
External objects in Salesforce allow you to access data stored outside of Salesforce in real-time via external data sources, using Salesforce Connect. They behave like regular Salesforce objects, but the data is not stored in Salesforce, and queries are made in real-time to the external system. This is particularly useful for integrating with legacy systems or other external databases without importing the data into Salesforce.
28. What are the typical integration patterns used with Salesforce?
Typical integration patterns with Salesforce include:
- Batch Data Synchronization: Regularly syncing data between Salesforce and other systems in batch mode.
- Real-Time Synchronization: Immediate data sync when records are created or updated, using webhooks or platform events.
- Remote Call-In: External systems call into Salesforce using Salesforce APIs to retrieve or update data.
- User Interface Integration: Embedding external application UIs within Salesforce or vice versa, to provide a seamless user experience.
29. How do you choose between REST and SOAP APIs for integration?
- REST API is generally preferred for web applications due to its simplicity, flexibility, and compatibility with web standards. It supports both XML and JSON formats and is ideal for mobile applications and any integration that requires OAuth for authentication.
- SOAP API is suited for enterprise-level integrations that require high levels of security and transactions that involve multiple calls in a single request. It is more rigid but reliable for complex operations.
30. What considerations should be made when integrating Salesforce with ERP systems?
When integrating Salesforce with ERP systems, consider:
- Data consistency and integrity across systems.
- The volume of data to be synchronized and the frequency of updates.
- Security and compliance requirements, ensuring sensitive data is protected.
- Choosing the right integration tools and technologies (middleware, APIs).
- Planning for potential system downtime or performance impacts during integration.
31. Describe how you would secure data transmitted between Salesforce and external systems.
To secure data transmitted between Salesforce and external systems, follow these practices:
- Use of Secure Protocols: Always use HTTPS for web services, SFTP for file transfers, and TLS for all connections to ensure data is encrypted in transit.
- Authentication and Authorization: Implement OAuth for secure, token-based authentication. Ensure only authorized users and systems can access data.
- Data Masking and Encryption: Apply field-level encryption and consider masking sensitive data when it is unnecessary for the external system to have access to detailed information.
- Monitoring and Logging: Monitor and log all data transmissions to detect and respond to potential security threats or data breaches.
32. What is an Integration User, and when would you use it?
An Integration User is a dedicated Salesforce user account used specifically for integrations between Salesforce and external systems. This user has permissions tailored to the needs of the integration, limiting access to only the necessary data and actions. Use an Integration User to:
- Enhance Security: By isolating integration activities from regular user operations.
- Audit and Track: Easier auditing and tracking of data changes and system interactions caused by automated processes.
- Compliance: Meet compliance requirements by controlling and limiting data access through specific profiles and roles.
Common performance bottlenecks in Salesforce applications include:
- Complex SOQL Queries: Queries that do not use indexes or that scan large data volumes can slow down performance.
- Apex Governor Limits: Hitting Apex CPU time limits, SOQL query limits, or DML limits can cause processes to fail.
- Page Load Times: Visualforce pages or Lightning components with complex logic or excessive server calls can delay page rendering.
- Data Skew: Large numbers of records associated with a single record (account or parent record) can degrade performance.
The Developer Console in Salesforce provides tools to troubleshoot performance issues:
- Debug Logs: Set up debug logs to trace the execution of code and identify where delays or problems occur.
- Performance Analysis: Use the Performance tab to analyze the load times of Visualforce pages and understand where time is being spent.
- SOQL Query Optimization: Review SOQL queries from the logs to find inefficient queries that need optimization.
- Execution Overview: Use the Execution Overview tab to view detailed information about the execution of your code, including timings and resource usage.
Limitations of Salesforce report performance include:
- Data Volume: Large volumes of data can slow down report generation.
- Complex Calculations: Reports with complex formula fields or multiple groupings can be slow.
- Simultaneous Requests: High numbers of users running reports simultaneously can affect performance.
To overcome these limitations:
- Summary Fields and Indexing: Use summary fields and ensure fields used in filters and joins are indexed.
- Limit Data Scope: Reduce the scope of the data in the reports where possible.
- Scheduled Reports: Schedule reports during off-peak hours to reduce load on the system.
36. Describe the process to optimize SOQL queries.
To optimize SOQL queries:
- Use Indexes: Ensure that fields used in WHERE clauses are indexed.
- Selective Queries: Make queries selective by ensuring that they filter a significant percentage of the data, typically using indexed fields.
- Batch Large Queries: For very large data sets, consider batching the queries or using asynchronous methods to process the data in smaller chunks.
- Avoid SOQL in Loops: Never place SOQL queries inside FOR loops to prevent hitting governor limits.
37. How do you use Salesforce’s Execution Governors and Limits?
Salesforce imposes Governor Limits to manage resources on the platform. To use these limits effectively:
- Understand the Limits: Be aware of the various limits, such as the number of SOQL queries, DML statements, and CPU time per transaction.
- Optimize Code: Write efficient Apex code to perform within these limits, such as bulkifying Apex triggers and using batch processes.
- Monitor and Test: Regularly monitor your application’s performance and conduct load testing to ensure it operates within these limits under peak loads.
38. What is the recommended approach for deploying changes in Salesforce?
The recommended approach for deploying changes in Salesforce includes:
- Use of Sandboxes: Develop and test changes in sandbox environments before deploying to production.
- Version Control: Use version control systems to manage changes and track revisions.
- Change Sets: Use change sets for transferring changes between Salesforce orgs, or use more sophisticated CI/CD tools for automated deployments.
- Testing: Perform comprehensive testing, including unit tests, integration tests, and UAT to ensure functionality and performance.
39. How do you manage version control with Salesforce development?
Manage version control in Salesforce development by:
- Using Git: Utilize a version control system like Git to track changes in your Salesforce code and configurations.
- Integrate IDEs: Use integrated development environments (IDEs) like VS Code with Salesforce extensions that support version control operations.
- Branch Strategy: Implement a branching strategy that supports your development workflow, such as feature branching or Git flow.
40. What are the best practices for Salesforce environment management?
Best practices for Salesforce environment management include:
- Multiple Environments: Use multiple environments (e.g., development, testing, staging, and production) to ensure changes are thoroughly tested before going live.
- Environment Specific Configuration: Manage configuration settings that are specific to each environment.
- Monitoring and Auditing: Regularly monitor and audit environments for performance and compliance.
41. Describe strategies for effective test automation in Salesforce.
Effective test automation in Salesforce can be achieved by:
- Using Apex Test Classes: Develop comprehensive test classes in Apex to cover all use cases, including positive and negative scenarios.
- Test Data Setup: Utilize
@testSetup methods to create test data for multiple test methods, ensuring tests do not depend on data in your production environment.
- Mocking External Calls: Implement mocking frameworks to simulate external API calls, avoiding dependencies on external systems during testing.
- Continuous Integration: Integrate a CI pipeline to automatically run tests whenever changes are committed, ensuring immediate feedback on the impact of changes.
42. How do you ensure a smooth user acceptance testing (UAT) process?
To ensure a smooth UAT process:
- Clear Criteria: Establish clear acceptance criteria with stakeholders before UAT begins.
- Comprehensive Training: Provide training sessions and detailed documentation to UAT participants to familiarize them with the functionality being tested.
- Dedicated Test Environment: Set up a dedicated UAT environment that mirrors the production environment as closely as possible.
- Feedback Mechanism: Implement an efficient mechanism for users to report issues and provide feedback during UAT.
43. Describe an approach for handling multi-language and multi-currency support in Salesforce.
For multi-language and multi-currency support:
- Translation Workbench: Use Salesforce’s Translation Workbench to manage translations for custom labels, picklist values, and other UI elements.
- Custom Labels: Utilize custom labels for storing text in multiple languages, which can be referenced in Visualforce pages and Apex code.
- Currency Management: Enable Advanced Currency Management for handling date-specific exchange rates if business operations require managing records in multiple currencies over time.
- Locale Settings: Configure locale settings for users to ensure that date formats, number formats, and other locale-specific settings are correctly displayed.
44. How would you architect a solution for real-time analytics in Salesforce?
Architecting a solution for real-time analytics in Salesforce:
- Salesforce Reports and Dashboards: Utilize real-time reports and dashboards for up-to-date data visualizations.
- Streaming API: Implement Salesforce Streaming API to receive real-time data updates pushed to client applications.
- Einstein Analytics: Leverage Salesforce Einstein Analytics (Tableau CRM) for advanced analytics capabilities, including AI-driven insights and predictions.
- External Tools: Integrate with external real-time analytics platforms if higher scalability or specialized analytic capabilities are needed.
45. What are considerations for implementing Single Sign-On (SSO) with Salesforce?
Considerations for implementing SSO with Salesforce include:
- Identity Provider (IdP): Choose a reliable IdP that supports standards such as SAML 2.0 or OAuth.
- User Directory Integration: Ensure that your user directory (like Active Directory or LDAP) is integrable with Salesforce for seamless user management.
- Security Protocols: Implement robust security protocols to protect identity data and authentication tokens.
- Failover and Redundancy: Plan for failover scenarios to ensure that SSO functionality remains available even if one system goes down.
46. How do you approach the design of a Salesforce solution that must comply with GDPR?
To design a Salesforce solution compliant with GDPR:
- Data Minimization: Only collect data that is absolutely necessary for the operation of the business.
- User Consent: Implement mechanisms to capture and manage user consent for data collection and processing.
- Data Subject Rights: Ensure the system allows users to exercise their rights such as data access, rectification, erasure, and portability.
- Security Measures: Apply strong security measures to protect personal data, including encryption, auditing, and monitoring.
47. What are the considerations for using Blockchain technology in a Salesforce solution?
Using Blockchain technology in Salesforce involves:
- Use Case Identification: Identify processes that benefit from decentralization and immutable record keeping, such as supply chain management or identity verification.
- Integration Complexity: Assess the complexity of integrating Blockchain with existing Salesforce infrastructure.
- Performance and Scalability: Consider the impact of Blockchain on system performance and scalability, particularly in terms of transaction speed and data volume.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure compliance with regulatory requirements, especially those related to data privacy and security.